Primary And Secondary Prevention Of Cardiovascular Disease
Primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Despite the lack of robust supportive evidence aspirin was recommended and used extensively for primary prevention in patients at higher risk for cardiovascular events. This is achieved by maintaining a healthy lifestyle choice such as diet and exercise. A practical evidence-based approach Despite the fact that we possess highly effective tools for the primary and secondary prevention of myocardial infarction and other complications of atherosclerosis coronary heart disease remains the most common cause of death in our society.
Of cardiovascular disease we suggest low-dose aspirin 75-100 mgd in patients aged 50 years. 30 Secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease includes patients with prior CABG 311. Pharmacological blood pressure lowering for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease across different levels of blood pressure.
And the proportion of patients eligible for lipid screening when the age cutoffs of the 2012 and 2016 Canadian. Studies were identified by searching MEDLINE EMBASE and Cochrane databases using synonyms and MeSH Medical. Other outcomes included a decreased number of cardiovascular events improved lipid profile and eating habits decreased weight and increased physical activity.
People with established CHD CeVD or peripheral vascular disease secondary prevention. Proportion of patients who were taking statins for primary or secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease CVD who did not have evidence of CVD recorded in their charts and who underwent lipid screening. ARRIVE ASCEND ASPREE demonstrated modest to no benefit in preventing cardiovascular events and mortality with aspirin use for primary prevention.
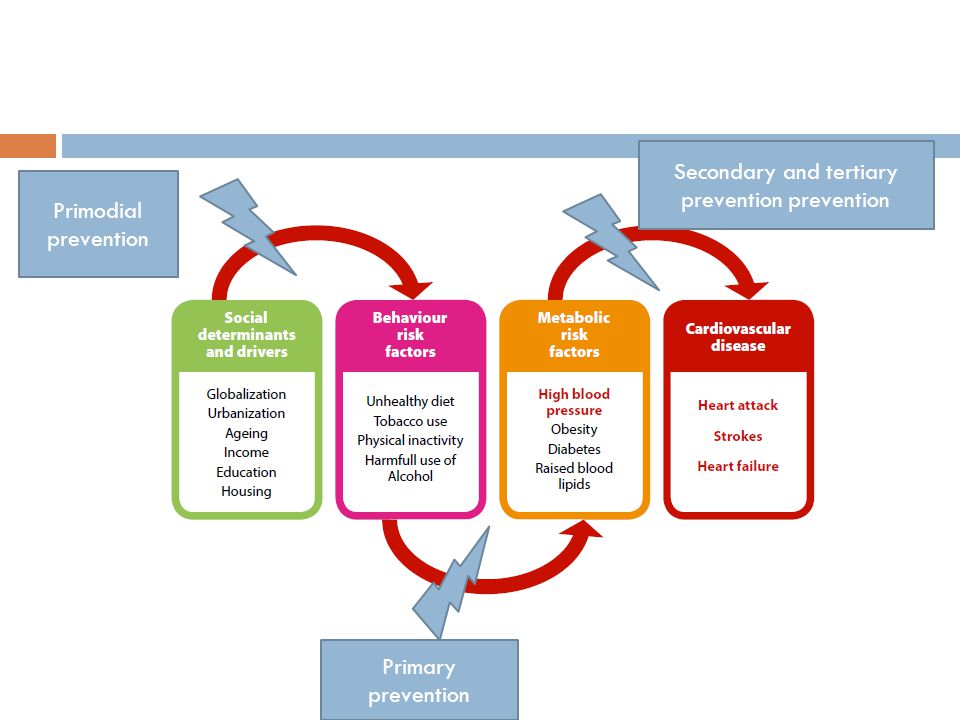
20 Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Over no aspirin therapy Grade 2B. Secondary prevention focuses on reducing the impact of the disease by early diagnosis prior to any critical and permanent damage.
Consequently primary prevention study populations range from healthy to subjects with evident symptoms of cardiovascular disease and in secondary prevention from relatively vague symptoms to postMI or stroke. Primary prevention refers to the steps taken by an individual to prevent the onset of the disease. These findings suggest that a fixed degree of pharmacological blood pressure lowering is similarly effective for primary and secondary prevention of major cardiovascular disease even at blood pressure levels currently not considered for treatment.
For patients with established coronary artery disease defi ned as patients 1-year post-acute coronary. A total of 1074 studies were identified with the database search.
Primary To quantify the effects of PCSK9 inhibitors on CVD all-cause mortality myocardial infarction and stroke compared to placebo or active treatments for primary and secondary prevention.
Distribution of statins among age groups. The essential first step for secondary CVD prevention in primary care is the accurate identification of those patients at greatest risk by establishing disease registers for CHD and stroke. Persons without symptomatic cardiovascular disease. For patients with established coronary artery disease defi ned as patients 1-year post-acute coronary. 30 Secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease includes patients with prior CABG 311. In fact unambiguous definitions of primary and secondary prevention. Having established registers practices need to initiate conduct and repeat clinical audit to ensure that the stipulated interventions are actually offered to those on the CVD registers. There is emerging evidence that Internet-based interventions may reduce cardiovascular risk in cardiac patients and in populations with a heightened risk of CVD. Studies were identified by searching MEDLINE EMBASE and Cochrane databases using synonyms and MeSH Medical.
Proportion of patients who were taking statins for primary or secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease CVD who did not have evidence of CVD recorded in their charts and who underwent lipid screening. Choice of antithrombotic therapy. For patients with established coronary artery disease defi ned as patients 1-year post-acute coronary. More recently in 2018 results of three randomized controlled trials. These findings suggest that a fixed degree of pharmacological blood pressure lowering is similarly effective for primary and secondary prevention of major cardiovascular disease even at blood pressure levels currently not considered for treatment. Over no aspirin therapy Grade 2B. Appropriate use of primary secondary and tertiary CVD prevention strategies including education to modify lifestyle risks individualized antiretroviral treatment regimens to achieve serum lipid targets and use of additional lipid-modifying strategies to minimize a patients overall CVD risk profile will be important throughout the treatment lifecycle.







































Posting Komentar untuk "Primary And Secondary Prevention Of Cardiovascular Disease"